A field of cannabis plants. Image Courtesy of Adobe Stock.
Cannabis has been used for medicinal and recreational purposes for thousands of years, and it has been legalized for medical or recreational use in many countries around the world. Despite the widespread use of cannabis, there is still ongoing debate about the potential health effects of chronic cannabis use.
In this blog post, we will explore the effects of chronic cannabis use on general health, including the impact on the brain, heart, lungs, immune system, and mental health.
Effects on the Brain
The active ingredient in cannabis, delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, which can cause a range of effects, including altered perception, impaired coordination, and changes in mood. Chronic cannabis use can lead to a variety of long-term effects on the brain, including memory impairment, reduced attention span, and decreased motivation.
A study published in the Journal of Neuroscience found that chronic cannabis use can lead to changes in the structure of the brain, particularly in the areas responsible for memory and emotion regulation. Another study published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research found that chronic cannabis use was associated with reduced brain volume in the hippocampus, which is important for memory and spatial navigation.
Adolescents and Cannabis
The developing brain is particularly vulnerable to the effects of cannabis. Adolescents who use cannabis regularly may experience negative effects on brain development, including impaired cognition and memory, decreased attention span, and reduced motivation. Studies have also shown that chronic cannabis use during adolescence can lead to structural and functional changes in the brain, particularly in areas related to memory and learning. Additionally, cannabis use during adolescence has been associated with an increased risk of developing psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia and depression, later in life. Therefore, it is important for parents and educators to educate young people about the potential risks associated with cannabis use and to encourage them to avoid or delay use until their brains have fully developed.
Effects on the Heart
Cannabis use can have short-term effects on the heart, such as increased heart rate and blood pressure. These effects typically last for a few hours and can increase the risk of heart attack or stroke in people with pre-existing cardiovascular disease. Chronic cannabis use has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, particularly in young people.
A study published in JAMA Cardiology found that young adults who used cannabis regularly had a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease later in life, even after controlling for other risk factors such as tobacco use and BMI.
Effects on the Lungs
Smoking cannabis can have similar effects on the lungs as smoking tobacco, such as bronchitis, chronic cough, and wheezing. Chronic cannabis use has also been linked to an increased risk of lung cancer, although the evidence is not as strong as for tobacco use.
A study published in the International Journal of Cancer found that people who smoked cannabis regularly for more than 10 years had an increased risk of lung cancer, even after controlling for tobacco use.
Effects on the Immune System
Cannabis use can affect the immune system, both positively and negatively. THC has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which may be beneficial for people with autoimmune diseases or other inflammatory conditions. However, chronic cannabis use can also suppress the immune system, making people more susceptible to infections.
A study published in the Journal of Leukocyte Biology found that chronic cannabis use can lead to a decrease in the number and function of immune cells, which can increase the risk of infections.
Effects on Mental Health
Cannabis use has been linked to a range of mental health problems, including anxiety, depression, and psychosis. Chronic cannabis use can also lead to addiction, which can have a negative impact on mental health and overall well-being.
A study published in JAMA Psychiatry found that frequent cannabis use in adolescence was associated with an increased risk of depression and suicidal behavior in young adulthood. Another study published in The Lancet Psychiatry found that cannabis use was associated with an increased risk of psychosis, particularly in people with a genetic predisposition to the condition.
Effects On the Oral Cavity
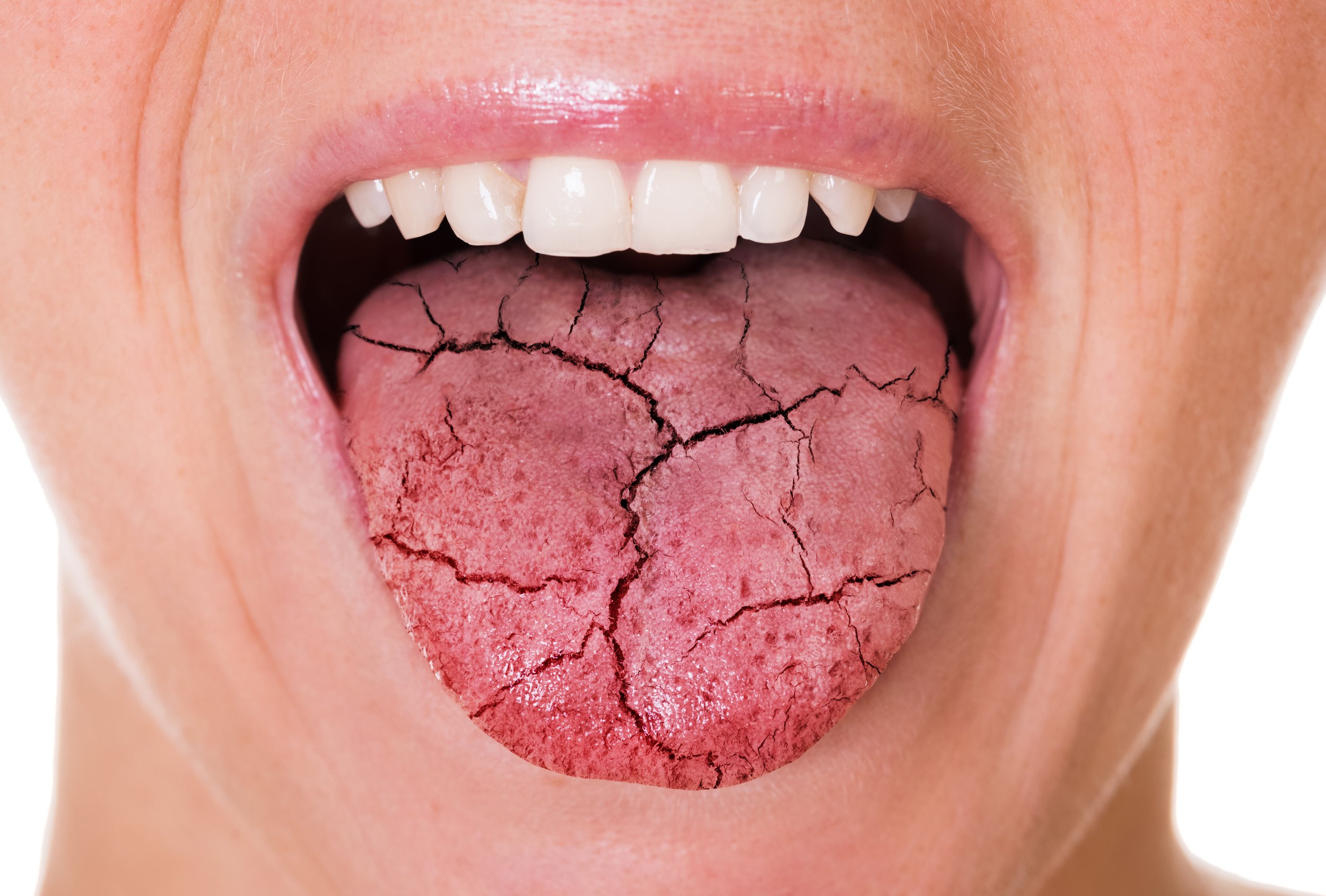
Chronic cannabis use can also have negative effects on the oral cavity. Smoking cannabis can cause dry mouth, which can increase the risk of tooth decay and gum disease. Additionally, smoking cannabis can irritate the gums and cause inflammation, which can lead to gingivitis and periodontal disease. A study published in the Journal of Periodontology found that chronic cannabis use was associated with an increased risk of periodontal disease, even after controlling for other risk factors such as tobacco use and oral hygiene. Therefore, it is important for individuals who use cannabis to maintain good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, and to seek dental care if they experience any oral health issues.
Conclusion
Chronic cannabis use can have a range of effects on general health, including the brain, developing brain, heart, lungs, immune system, mental health and oral health. While some of these effects may be beneficial for certain conditions, such as anti-inflammatory properties for autoimmune diseases, the risks associated with chronic cannabis use should be carefully considered.
It is important to note that the research on the health effects of cannabis is still evolving, and more studies are needed to fully understand the potential risks and benefits.
This blog article was written with the assistance of ChatGPT.